| REALoc About Help |
|
|
REALoc: Reliable and effective methods to assist predicting human protein subcellular localization |
|---|
|
Drug development and investigation of protein function both require an understanding of protein subcellular localization. We developed a system, REALoc, that can predict the subcellular localization of singleplex and multiplex proteins in humans. This system consists of two systematic frameworks that integrate one-to-one and many-to-many machine learning methods and use se-quence-based features, including amino acid composition, surface accessibility, weighted sign aa index, and sequence similarity profile, as well as gene ontology function-based features. REALoc can be used to predict localization to six subcellular compartments (cell membrane, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi, mitochondrion, nucleus, and extracellular). REALoc yielded a 75.3% absolute true success rate during five-fold cross-validation and a 57.1% absolute true success rate in an independent database test, which was >10% higher than four other prediction systems. Lastly, we analyzed the effects of Vote and GANN models on singleplex and multiplex localization prediction efficacy. 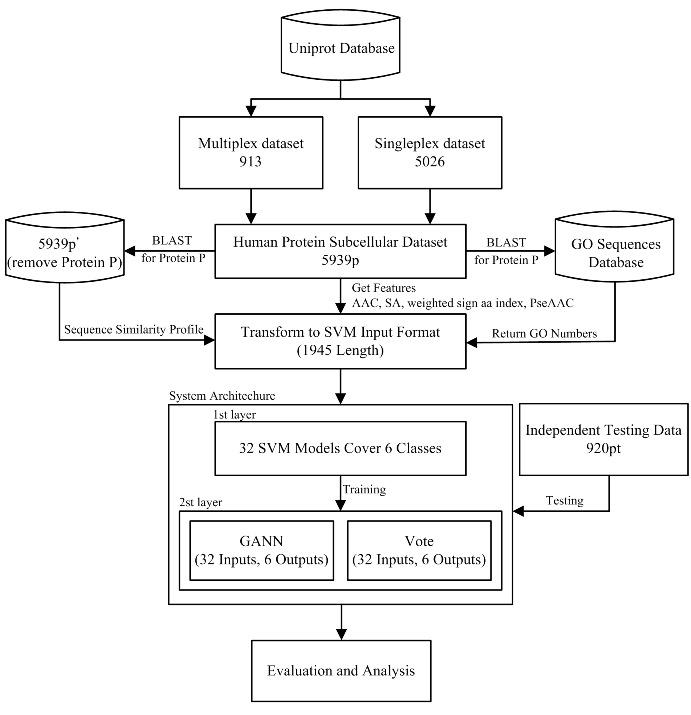 Reference: Chi-Hua Tung, Chi-Wei Chen, Han-Hao Sun, Yen-Wei Chu* (2017) Predicting human protein subcellular localization by heterogeneous and comprehensive approaches, PLoS ONE, 12(6):e0178832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178832.Download dataset |
Home
| Natural Computing & Bioinformatics Laboratory ( NCB Lab.), Institute of Genomics and Bioinformatics, National Chung Hsing University, Taiwan. |
| For questions and comments, please contact:ywchu@nchu.edu.tw. |
| Last update: November 6, 2015 |
